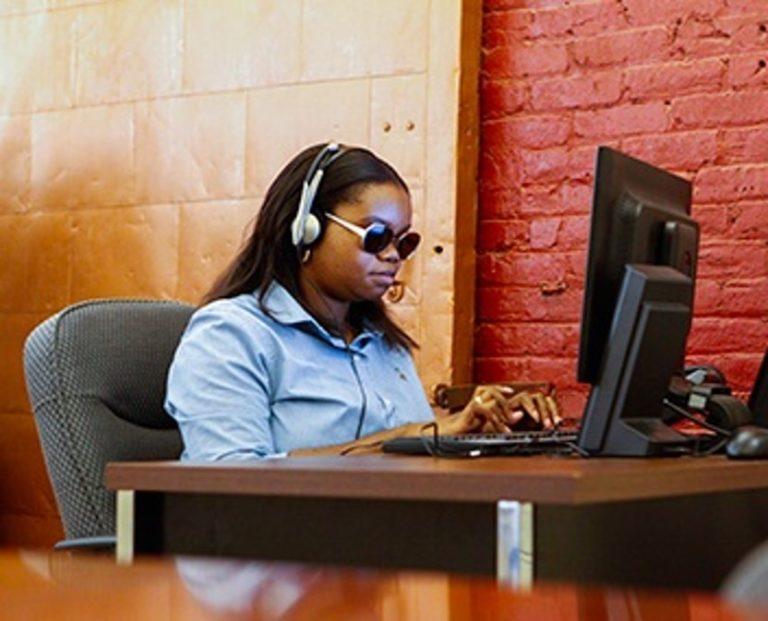

Screen Readers
Screen readers enable blind or visually impaired users to read the text that is displayed on the screen of a computer, smartphone or tablet with a speech synthesizer or braille display.

Assistive technology devices are amazing enablers for persons with disabilities, and in fact now considered essential for quality inclusive education. However, they do not work in isolation. Persons with disabilities using assistive technology need an enabling barrier-free environment and infrastructure that allows them to be functional in the educational institution with the help of Assistive Technology devices.
Technology is redefining what a person with disability can or cannot do. New developments in the field of Assistive Technology devices enhances functional capability of persons with disabilities that they have lost due to their physical or sensory impairment.
For example, use of smart phones or computers with the help of screen reading software enable persons with blindness or low vision to be able to read and write in mainstream script. This enables them to have written communication with their teachers, write assignments and examinations without the need of scribes and access to reading materials if made available in accessible digital format. Below are few examples of such enabling technology solutions. Access to these devices to learners with disabilities would enable their equal and full participation in inclusive education.

Screen readers enable blind or visually impaired users to read the text that is displayed on the screen of a computer, smartphone or tablet with a speech synthesizer or braille display.

A screen magnifier is software that presents enlarged screen content for people with visual impairments so they can better see words and images. This type of assistive technology is useful for people with some functional vision; people with little or no functional vision usually use a screen reader.

Braille is a tactile script that enables person with blindness to read written text using their fingers. Traditionally braille is embossed on thick paper.
Read Aloud is a accessibility feature that uses text-to-speech (TTS) technology to convert text to audio. Read-aloud feature benefits learners with low vision, and is often used by those with specific learning disabilities such as dyslexia.
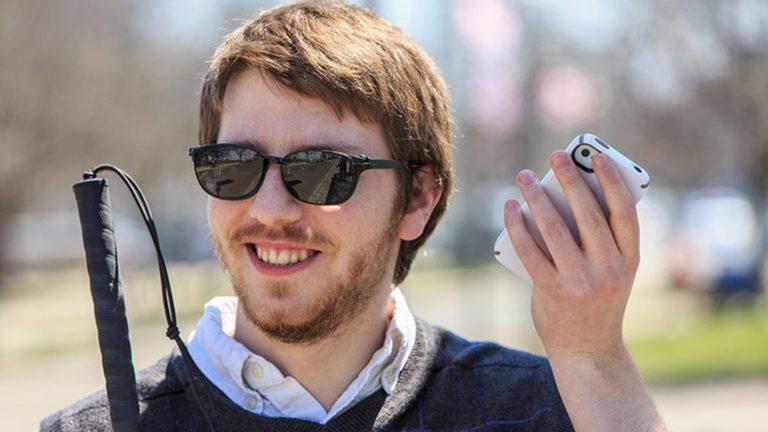

Read Aloud is a accessibility feature that uses text-to-speech (TTS) technology to convert text to audio. Read-aloud feature benefits learners with low vision, and is often used by those with specific learning disabilities such as dyslexia.

Learners with disabilities need different tools for taking notes in a class or writing in examinations.
In the system of inclusive education, an educator has the responsibility of acknowledge diversity among students and provide reasonable accommodation to them. This enables them to get equal opportunity to get quality education. Disability is one of such diversity.
For example, if a person with blindness is in the class, it becomes responsibility of the educator to recommended readings and handouts are made available in accessible format to him/her. In almost all such cases, everything that is accessible to persons with disabilities is also better experience for everyone. Here are few technology solutions that would help educators to provide reasonable accommodation to learners with disabilities.

Even though sight-reading is what most people think of when they think of reading, there are two other types of reading: reading through touch—using Braille to access text, and reading through audio —listening to narrated content or using computer generated text-to-speech.
Persons with print disabilities cannot read hard copy book or photo-copy sheets or digital text stored as an image. These materials need to be converted into editable digital text documents to make them readable by persons with print disabilities on their devices.
Assistive Technology devices in the hands of learners with disabilities cannot be effective if used in isolation. An enabling environment in the institution is essential to enable AT devices to remove functional limitations of persons with disabilities.
For example, a wheel chair would be useful only if we have ramps and lifts installed in the building. Similarly, persons with print disabilities can read and write themselves with the help of computers and smartphones with screen reading software or with refreshable braille display. However, if the web site of the institution, and digital documents and instructional materials are not provided to them in accessible format, then best of the devices would become useless. Therefore, it is essential for an institution to plan for the holistic solution to be provided to learners with disabilities. The articles in this section can get you started.
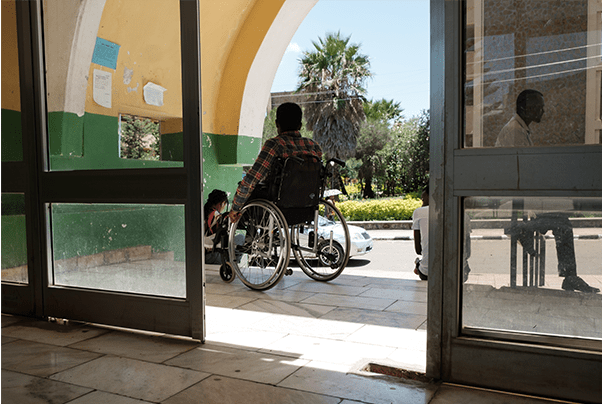

Educational institutions have the responsibility of ensuring that all learners including persons with disabilities have equal access to all facilities and services. Technology can play a role in accommodating different disabilities.

Websites, Learning Management Systems, online Libraries and any information distributed through the internet needs to be easy to use for everyone including learners with disabilities.
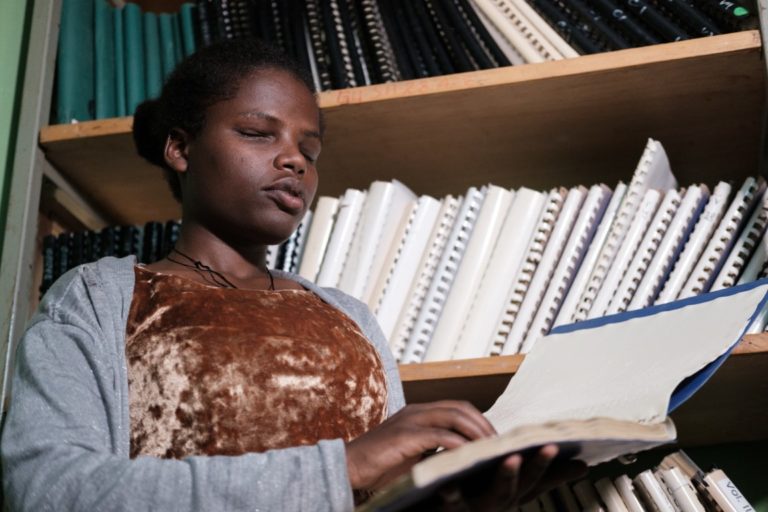

Libraries provide us with a vast resource of knowledge whereby a student can access books, journals, periodicals, newspapers and other learning resources. To make the library inclusive ensures that persons with disabilities have equal access to both the physical and digital library.

In past years students with print disabilities relied on university resource units, non-profit organizations or even volunteers to provide access to their academic texts. Fortunately, this is changing for the better.